Many times, in the fast paced business world, companies are fraught, with challenges, thought-provoking and complex problems that sometimes leave even major corporations feeling stuck, unable to move forward. Recognising this issue across domains, a solution emerged –design thinking problem solving process. Reputable and noteworthy organisations have embraced this method, and it has been revealed to be very effective. Organisations in this category include IBM and Netflix. Design thinking process helps them understand what their users want and respond in such a manner. However, several misconceptions follow the design thinking process, which further clarity will be made on in this article.
Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process is a method for coming up with innovative solutions to problems while keeping users’ and consumers’ wants and preferences in mind.
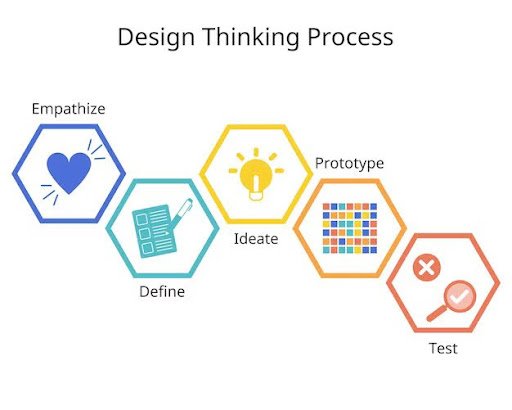
The design thinking process follows a similar method to the creativity process. In a creative process, first there is preparation, where you prepare, and understand the problem. Then comes incubation, where you imagine and generate various ideas and concepts. Next is illumination, where you refine and develop your ideas further. Finally, you illustrate and verify your creative ideas.
The design thinking process works in a similar manner. The first step is to empathize with your users. This simply means understanding them on a deeper level. Here, you meet with some of your users and relate to them, you can even carry out various interviews and explore with them to gain a deeper understanding of what the problem is. It is similar to putting yourself in another person’s position to understand situations from their viewpoint.
The second stage is to define what you have learned from your exploration so far. Here, you ask yourself the “Five Whys” – What the problem is, who it is affecting, where the problem is most felt, why the problem matters, and when it occurs. It is akin to finding patterns in your empathetic journey and providing answers to the questions arising from your exploration. Upon completing this stage, you begin to ideate. It is a flexible and collaborative process that encourages trying new things and learning from your mistakes. With design thinking, you brainstorm numerous ideas, create prototypes to test them, and continually improve until you find the optimal solution.
After the ideation stage comes the prototyping stage. This is similar to the illustration stage in a creative process. Here, you illustrate the solution you arrived at or your desired product. It should be mentioned that design thinking is applicable to a wide range of problems, including those involving the creation of new products, the improvement of existing services, and societal difficulties. In general, it centres on thinking creatively to find workable and approachable solutions.
Finally, the last step is testing and verifying your ideas, products, or solutions to ensure they meet the needs of consumers as envisioned.
Common Misconceptions
Despite its increasing popularity, misconceptions about the design thinking process are common. Let us dispel a few frequent misconceptions:
Misconception 1: Only Designers Can Use Design Thinking.
This misconception is definitely not true. Using the design thinking process does not require you to be a designer. You can use it even as an individual because it is a problem-solving technique that everyone can learn and utilise, regardless of background or job position.
Misconception 2: Design thinking is just about making things look pretty.
This is wrong. The design thinking process goes beyond making things visually appealing. It is about understanding what people need and creating solutions that work well for them.
Misconception 3: Design thinking does not produce results.
This is very wrong. By incorporating this method, major corporations like Apple have been able to remain at the forefront of their industry for so many years now. Other corporations, like Airbnb and IBM, also use it to effectively meet the needs of their consumers.
Misconception 4: Design thinking is only for physical products.
Not only can the design thinking process be applied to physical products, but to many other areas as well. It can enhance procedures, services, and even user experiences, such as accessing an application or website.
Misconception 5: Design thinking is a very complex problem and needs experts.
This is very wrong. It is not necessary to be an expert to apply design thinking process. It is more about collaborating with others, trying new things, and maintaining an open mind.
To put it simply and clear up doubts, the design thinking process is an adaptable and inclusive approach to tackling problems. By letting go of these misconceptions, whether you are creating a new product, enhancing an existing one, or just managing day-to-day problems, the design thinking process is the method to use.
True Statements about the design thinking process
The design thinking process is like a gentle breeze in the world of problem-solving, bringing a sense of openness and collaboration. Join us, as we take a stroll through some true statements about this process:
Design thinking nurtures collaboration
The design thinking process is about unitedly collaborating to find solutions to problems. It invites individuals with diverse backgrounds – be they designers, engineers, or regular people – to collaborate together towards a common objective. The cooperative atmosphere fosters a supportive setting where all contributions are appreciated and honoured.
Design thinking begins with Empathy
Empathy is a must in design thinking. This involves comprehending the emotions and experiences of others and acting on them. By comprehending these experiences, we can gain a valuable understanding of what they require and want. This compassionate method guarantees that our solutions are based on true compassion and comprehension.
Design thinking brings about continuous improvement
The design thinking process continually guides us towards enhanced performance. It supports the idea of progressively making tiny, moderate progress rather than immediately aiming for perfection. We develop prototypes, collect feedback, and make adjustments gradually during the process. This gradual iterative process enables us to develop our ideas smoothly, without hurrying or pressuring ourselves.
In design thinking, failure is met with compassion
In the design thinking process, failure is an opportunity to do better rather than a harsh critic. Failure is understood as a normal aspect of the creative process. Every mistake is approached with a curious mindset and a readiness to absorb new knowledge, leading us towards kinder and stronger solutions.
Design thinking births creativity
The design thinking process is comparable to a gentle whisper of inspiration, guiding us gently towards creative solutions. It inspires us to engage in play, discover, and envision fresh opportunities. By utilising soft approaches such as brainstorming and doodling, we access our natural creativity and generate gentle, original concepts.
To sum up, the design thinking process is an illustrative method for approaching problems while embracing collaboration, empathy, failure, creativity, and growth. By adopting this process, we can create solutions that are conscious and satisfactory to the world.
Key Takeaways
- The design thinking process is an all-encompassing problem solving approach.
- The design thinking process is a team-oriented method that requires gathering people with different experiences to collaborate on a shared objective.
- The design thinking process has five (5) stages, namely; empathy, define, ideate, prototype, and testing.
- The process starts by practicing empathy, in which designers aim to comprehend the needs and experiences of the individuals they are creating for.
- In the design thinking process, failure is accepted as a normal aspect of the creative process, offering important chances for learning and shaping the creation of stronger solutions.
- The design thinking process promotes innovative problem-solving by questioning traditional thought and investigating different viewpoints.
- User feedback is essential in steering the incremental development of solutions, making sure they are focused on users and in line with actual needs and preferences.

